waveware Server
Overview
The waveware server is the basis of all waveware installations. Most adjustments are executed directly with the client programs, such as the DataManagement (e.g. the setup of the integrated web server) and the waveware Client. You will find below import maintenance functions and access possibilities which you can apply on the waveware server.
Client Connections
Each client application maintains a steady connection to the waveware server after the login. If this client connection is interrupted because of a network failure, the waveware Client will automatically restore the connection when the waveware server is available again. The waveware Client cannot be used during this server search. A notification will inform you about the connection attempts which are repeated every 15 seconds.

Click on the button 'Restore' to make a connection attempt. 'Exit' will close the waveware client.
If the connection cannot be restored, or if it has expired or is invalid, the message below appears, whereupon waveware is closed.
How long a Client keeps an inactive connection to the server can be customized for each Client. Open the DataManagement and click on the 'waveware Server' button to open the server settings. In the section 'Automatic logout' the corresponding entries can be made. The time span specified here must have elapsed before the waveware server terminates the respective connection.

 |
You can specify here the interval for the waveware FAT Client after which a user is considered inactive and is logged out. The user receives a notification after the specified period of time informing him/her that the session has expired and that the program is being closed. "2:00" is the default value for 2 hours. 48 hours is the maximum limit. |
 |
Captures the amount of time that must elapse before a user in the Mobile Client is considered inactive and the server connection is closed. The default is "01:00". More than 48 hours are not supported. If you frequently run waveware Mobile in the background, it can happen that sessions to the waveware server are interrupted, although the set runtimes of the client connections have not yet been reached. With most mobile devices, these unintentional disconnections can be prevented by deactivating the energy-saving/battery-saving settings for waveware Mobile.
|
 |
Defines the time span after which a logged in user is considered inactive and the connection is automatically closed by the server for the Web Client of the waveware server. Default is "01:00". A maximum of 48 hours can be specified. |
 |
If no explicit logout of the user takes place in the Web Client and instead for example, if only the browser window is closed or disconnected, the time specified here must elapse before the waveware server resets the session and releases the used web access license for another user. Prior to expiration, a session may be resumed at any time, e.g. when a network problem has been resolved. The default is estimated at 30 minutes. |
 |
Time that must expire before a user is considered inactive in DataManagement and the server connection is closed. "01:00" is the standard here and a maximum of 48 hours is possible. |
 |
Defines the interval for automatic logoff e.g. B. for system users like 'SystemHeartbeat', 'SystemSap' etc. and for Custom Pages. The standard here is "01:00" for one hour. A maximum of 48 hours is possible. |
In waveware Mobile and on the waveware Web, the waveware server cannot reliably detect, whether a session is still actively used or already inactive, because for example, the browser was closed. This is because with these two client variants no permanent connection to the waveware server is maintained. The time periods listed above act as a timeout - a session is discarded after a certain time has elapsed. Not always the regulation over timeout is satisfactory, because in this way access licenses are blocked for a long time.
From waveware 11.170.2118, there are Supervisor Options in the path "System\System(0)\waveware\Sessions" to replace unneeded but background active sessions.

For each client application, you can set whether any existing sessions should be discarded if the same user logs in again. Only the client type sessions are discarded, at which the user logs in again; So for example, if you log back in to the waveware Web, all web sessions will be removed; all mobile sessions will be removed when logging in to the mobile client, and so on. By default, this feature is disabled (all supervisor options disabled).
Protocol of the Client Connections
With waveware 11.190 the client/server protocol was changed from a custom binary serialization to 'gRPC', an RPC protocol-based framework developed by Google. The protocol offers the following advantages:
- Standardized framework instead of custom binary serialization
- Based on HTTP/2 (e.g. allows reverse proxies and application firewalls for all ports)
- Better compression and faster data exchange
- Can be used in all waveware clients equally (Windows client, mobile client and web client)
Till 11.200.3434, waveware had two gRPC interfaces to establish client connections: one based on the web server (default port 10000) and another gRPC-only interface (default port 17000). Both interfaces exposed exactly the same API. They only differed in that the integrated Kestrel web server or the gRPC library was used.
As of waveware 11.200.3434, the pure gRPC interface (default port 17000) has been dropped in order to simplify and standardize the configuration. The port can no longer be reached from the outside, but only locally via loopback.
Connection Establishment
In order to establish a connection from the client to the waveware server, information in the 'Server' field of the client login window is evaluated.

With the help of prefixes, you can activate various special features when establishing a connection directly via the client.
It is always recommended to establish an encrypted connection using "https". Further special features when setting up under 'Secure Client Connections'. If possible, avoid unencrypted connections ("http" and without a prefix).
| Prefix | Usage | Description |
|---|---|---|
| noproxy | noproxy://wavewarehost noproxy://wavewarehost:9090 |
Ignores any proxy server set in the local system. "noproxy" is available from waveware 11.200.2965.42. |
| web+http | web+http://wavewarehost:10000 web+http://wavewarehost |
Web gRPC with HTTP1/1 is used instead of gRPC with HTTP/2. |
| web+https | web+https://wavewarehost:443 web+https://wavewarehost:900 |
Web gRPC with HTTP1/1 over HTTPS (encrypted) is used instead of gRPC with HTTP/2. |
| noproxy+web+http | noproxy+web+http://wavewarehost:10000 noproxy+web+http://wavewarehost |
It uses Web gRPC with HTTP1/1 instead of gRPC with HTTP/2. Also ignores the system-wide proxy. "noproxy" is available as of waveware 11.200.2965.42. |
| http | http://wavewarehost:10000 | It uses gRPC with unencrypted HTTP/2. |
| https | https://wavewarehost:443 |
It uses gRPC with encrypted HTTP/2. |
Connection problems often occur because of the following reasons:
- Firewall or Reverse-Proxy does not support any HTTP/2
- Try with the prefix "web+https" or "web+http".
- Proxy does not support any HTTP/2- or local connections
- Try with the prefix "noproxy" or "noproxy+web+https" or "noproxy+web+http"
Secure Client Connections
gRPC is used for communication between the waveware server and its clients (see 'Protocol of the Connections'). However, connections via this protocol are unsecured by default; i.e. data transfers are unencrypted. With this default setting, data connections outside the internal network are risky and not recommended.
To encrypt data transmission in general, but especially for external access, encryption via HTTPS can be activated. This requires a setup and a valid SSL certificate. As of waveware 11.200.3434.39, the waveware web server is used to establish the connection. More information on setting up and securing the web server under 'waveware Server: Setting up Web Server'.
Setup
If you have a valid certificate (see also 'Certificate Creation with Let's Encrypt'), you have to make this known to the waveware server. To do this, open the waveware server settings via the menu ribbon 'Global settings' of the DataManagement and scroll to the 'GRPC settings' area.

You can make the settings for the certificate in two ways:
- Windows Certificate Store
As an alternative to using PEM certificates, the Windows certificate store can be used.
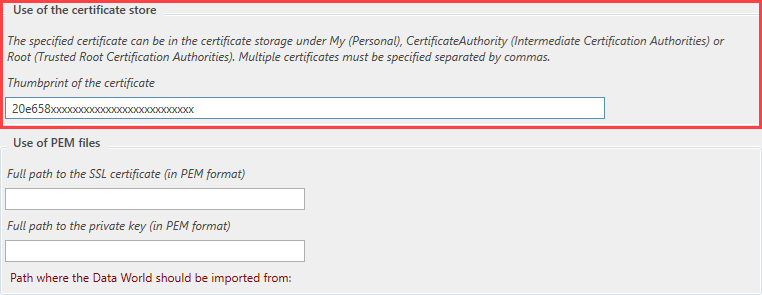
At this point you need to provide the certificate's fingerprint. You can also specify several certificates in the 'Thumbprint of the Certificate' field by separating them with a comma (comma-separated list). You do not have to specify a specific certificate store. The specified certificate is automatically searched for in the following certificate stores:Value Description CertificateAuthority Certificate stores of intermediate certification authorities. My Certificate store for personal certificates. Root Certificate store for trusted root certification authorities. It should be noted that the certificate selected in this way contains the private key and this can be exported. When importing the certificate into the certificate store, activate the import option 'Mark key as exportable'. After the import, the sentence "You have a private key for this certificate" appears in the certificate properties under 'General'. - Direct Path Specification
If a PEM (Privacy Enhanced Mail) certificate is to be used, the full path to the certificate and the full path to the private key file must be specified. Both paths are to be specified from the point of view of the waveware server. In addition, access rights to the paths are required for the user under which the waveware server service is running.

After saving the settings, you have to manually restart the waveware server service once so that the settings are applied.
Certificate Creation with Let's Encrypt
You can obtain certificates from any certification authority (CA) and integrate them into waveware. Let's Encrypt is a free, automated and open certification authority through which you can obtain free SSL certificates. Let's Encrypt uses the ACME protocol to check whether you control the domain to be certified. If this test is successful, the certificate is issued.
There are many different options for creating an SSL certificate using the ACME protocol (further information on the external website: https://letsencrypt.org/de/docs/client-options/). Examples for ACME clients under Microsoft Windows Server:
- Posh-ACME Client (https://github.com/rmbolger/Posh-ACME)
- WinCertes (https://github.com/aloopkin/WinCertes)
- win-acme (https://www.win-acme.com/)
Reset Setup
After setting up and restarting the waveware server, the Secure Client Connection can be established. Should when establishing the connection, e.g. if problems occur, e.g. with the DataManagement for the waveware server, you can reverse the setup in a few simple steps. Try to establish an insecure connection from the DataManagement to the waveware server (without the "tls://" or "https://" prefix in the server name) and check the setup carried out beforehand.
If a connection cannot be established even in an unsafe way, you can manually remove the settings from the 'user.config' file of the waveware server. If the waveware server is running under 'local system', you will find the file in the directory "C:\Windows\system32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\Loy_&_Hutz_Development_Gm\wavewareServerService64. ...\%Version of the Installation%\user.config"; otherwise analogous to this path in the AppData directory of the user under which the waveware server is running. The file has the following content:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
...
<userSettings>
<LoyHutz.Server.Core.Lib.Properties.Settings>
...
<setting name="GrpcCertificateSettings" serializeAs="String">
<value>CertFullPath=C:\Data\Cert\cert.pem;CertKeyPath=C:\Data\Cert\key.pem;CertStore=;CertThumbprint=</value>
</setting>
...
</LoyHutz.Server.Core.Lib.Properties.Settings>
</userSettings>
</configuration>
<setting name="GrpcCertificateSettings" serializeAs="String"> <value>CertFullPath=C:\Data\Cert\cert.pem;CertKeyPath=C:\Data\Cert\key.pem;CertStore=;CertThumbprint=</value> </setting>
Save the file and restart the waveware server. The facility was completely reset this way.
Secure Mobile Connections
The connection from the mobile client to the waveware server is also encrypted after certificates have been set up. To use the certificates, they must use a public certification authority (CA). Using certificates with local certification authorities is not possible and results in connection errors.
In addition, Android devices may have problems logging in via HTTPS with waveware MOBILE (1/2). In this case, the app displays "Login failed. Please try again later.". The error message “Trust anchor for certification path not found” is logged in the mobile log file. This error indicates an incomplete chain of trust.
As a rule, common root certificates such as “DigiCert Global Root G2” are installed on the devices. To complete the certificate chain, all intermediate certificates must be installed locally on the device.

The root certificate “DigiCert Global Root G2” is already present on the device as standard. However, the intermediate certificate “RapidSSL TLS RSA CA G1” is missing. After manually installing the intermediate certificate on the device, login with the app works over HTTPS.
The installation of the missing intermediate certificates can also be carried out centrally via an MDM (Mobile Device Management Software) in order to update all managed devices equally. Many MDM systems offer the ability to create configuration profiles. These profiles specify that intermediate certificates that were previously uploaded to the MDM should be installed on the target devices. Depending on the MDM system used and the device types (iOS, Android), additional settings can be made, e.g. whether the certificate is used for specific networks (WLAN or VPN) or whether it should be available globally on the device.
The configuration profiles containing the intermediate certificates are then distributed to the appropriate devices. After receiving the profile, the intermediate certificates are stored in the certificate store of the device. They are then available for waveware MOBILE (1/2).
Typically, you can use the MDM system to monitor the installation status on the devices and thus verify that the target devices have received the required intermediate certificates. If intermediate certificates expire or need to be updated, you can also control the exchange centrally via the MDM system.
Command Line Parameters
The 'wavewareServerConsole.exe' or 'wavewareServerService.exe' can be recalled with the following command line parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| -disableMutex | Closes the Mutual Exclusion (Mutex) in the waveware server. |
| -newSettings | Allows you to define new settings. |
| -webserverPrefix %Präfix% | Allows you to set the default prefixes of the web server, e.g. "http://+:10000/". |
| -webserverDocumentRoot | Sets the 'DocumentRoot' directory of the web server. |
| -disableWebserver | Deactivates the web server. |
| -logFile %Pfad% | Allows you to change the path to the log file. |
| -logAll | Activates the logging of all notifications (errors, warnings, information, etc). |
| -ruleDebugging | Activates the debugging of rules. |
| -captureChangedStatetables |
Activates the input of log entries when rules change data records. |
| -disableLocking | Completely deactivates locking of changed data records. |
| -disableChangelockExceptions | Deactivates notifications (locking exceptions) for already changed data records. |
| -logCache | Activates the logging of accesses to the query cache (new entries, empty, etc.). |
| -disableQueryCache | Deactivates the query cache. |
| -disableStatistics | Deactivates all statistics. |
| -disableCallStatistics | Deactivates the call statistics. |
| -disableQueryStatistics | Deactivates the query statistics. |
| -disableRuleStatistics | Deactivates the rule statistics. |
| -disableTaskStatistics | Deactivates the task statistics. |
| -showDebugInfo | Error reports ("exceptions") in detailed JavaScript exceptions with inner exceptions. |
| -shutdownOnLastConnectionLost | Activates the download of the server when the last connection is terminated. |
ServerPing
The program 'loyhutz.serverping.app.exe' is a help tool which can be used to monitor the waveware system and conduct a brief functional check thereof. You will find the tool in the program directory of the waveware servers. Use the prompts for opening and enter the following arguments.
Parameters
The ServerPing help tool can be executed with the following command line parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| -host | The adress of the waveware server, e.g. "localhost:10000"). |
| -mandantid | The client of the installation. |
| -installid | Install ID. |
| -user | Username with which the installation is to be accessed, e.g."Supervisor". |
| -password | User password. |
| -command | Defines the function of the enquiry with the following information:
ping - checks whether the waveware server is accessible and running. performancecounter - renders a list of the performance counters of the waveware server. locks - fetches a list of the locked objects in the waveware server. threads - displays a list of the threads in the waveware server. |
| -repeat | Shows whether the query is to be continuously repeated. |
| -delay | Shows the waiting time between queries. |
| -file | The file into which the data are to be written. |
Examples
The following command pings the waveware server uninterruptedly:
loyhutz.serverping.app.exe -command ping -startDelay 2000 -delay 0 -installid Installation -host localhost -repeat -mandantid 1 -user Supervisor -password ""
A further command continuously reads the performance counter and writes the values in the file 'values.csv':
loyhutz.serverping.app.exe -command performancecounter -host localhost:10000 -installid Installation -user Supervisor -password "" -command threads -repeat -file values.csv
Authentication
The waveware server provides you with a number of authentication methods. To these belong the login masks which can be used directly by the users and API functions which can be recalled with the HTTP to enable external programs to have access to the functions of the waveware server.
API Authentication
The following REST function must be called for you to use the API authorization:
http://localhost:10000/Api/Authenticate?username=Supervisor&password=&installid=Installation&mandantid=1
This function requires the login information. Note, however, that the values must be URL-coded. The following arguments can be used:
| Argument | Function | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| username | Login | Supervisor |
| password | Hash from user password and Serversalt | Test |
| installid | Install ID of the user | Installation |
| mandantid | Client ID of the user | 1 |
Once sent, the waveware server renders an HTTP reply containing a JSON object. This JSON object has three fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| error | Error report; empty when successful. |
| errorcode | Numerical error code;empty when successful. |
| securityToken | Session token. |
In the event of a successful authentication, the ‚securityToken‘ can be attached to all following queries to execute authenticated requests. A query can, for example, have the following look:
http://localhost:10000/1238/UnitTest/TestWebsessionValue.erb?securityToken=WertausResponse
Read more information about the REST functions 'REST InterfaceSchnittstelle'.
Application Example
The API authentication is illustrated in the following Javascript:
var salt = "";
// salt holen
$.ajax({
url: "Api/GetSalt",
dataType: "text",
success: function (result) {
// salt auswerten
salt = eval("(" + result + ")");
// passwort hash generieren
var pwHash = new jsSHA(unescape(encodeURIComponent(password)), "ASCII").getHash("SHA-256", "B64");
var transportHash = new jsSHA(pwHash + salt, "ASCII").getHash("SHA-256", "B64");
// authentifizierungs funktion aufrufen
$.ajax({
url: "Api/Authenticate",
data: "installid=" + encodeURIComponent(installId) + "&username=" + encodeURIComponent(username) + "&password=" + encodeURIComponent(transportHash) + "&mandantid=" + encodeURIComponent(mandantId),
dataType: "text",
success: function (result) {
result = checkForError(result);
if (result === false)
return;
}}));
The 'jsSHA' library is used to generate the hash (http://caligatio.github.io/jsSHA). The AJAX/REST requests are executes with the aid of jQuery.
